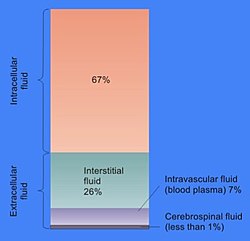
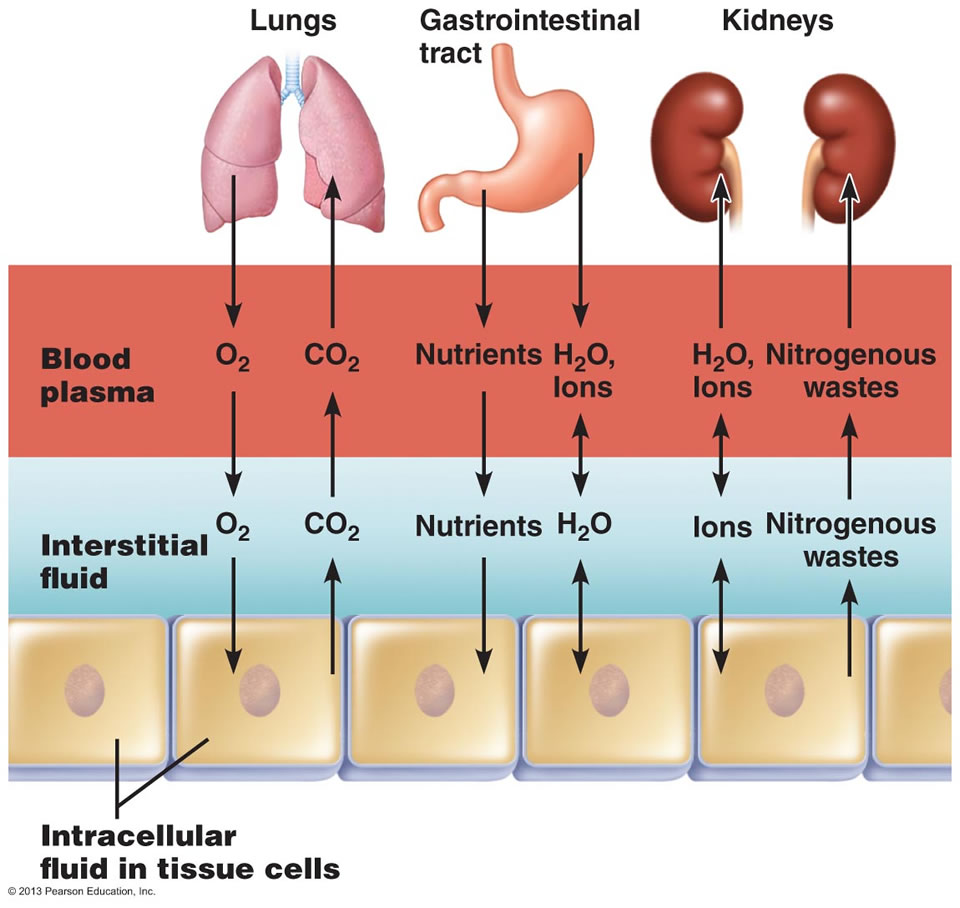
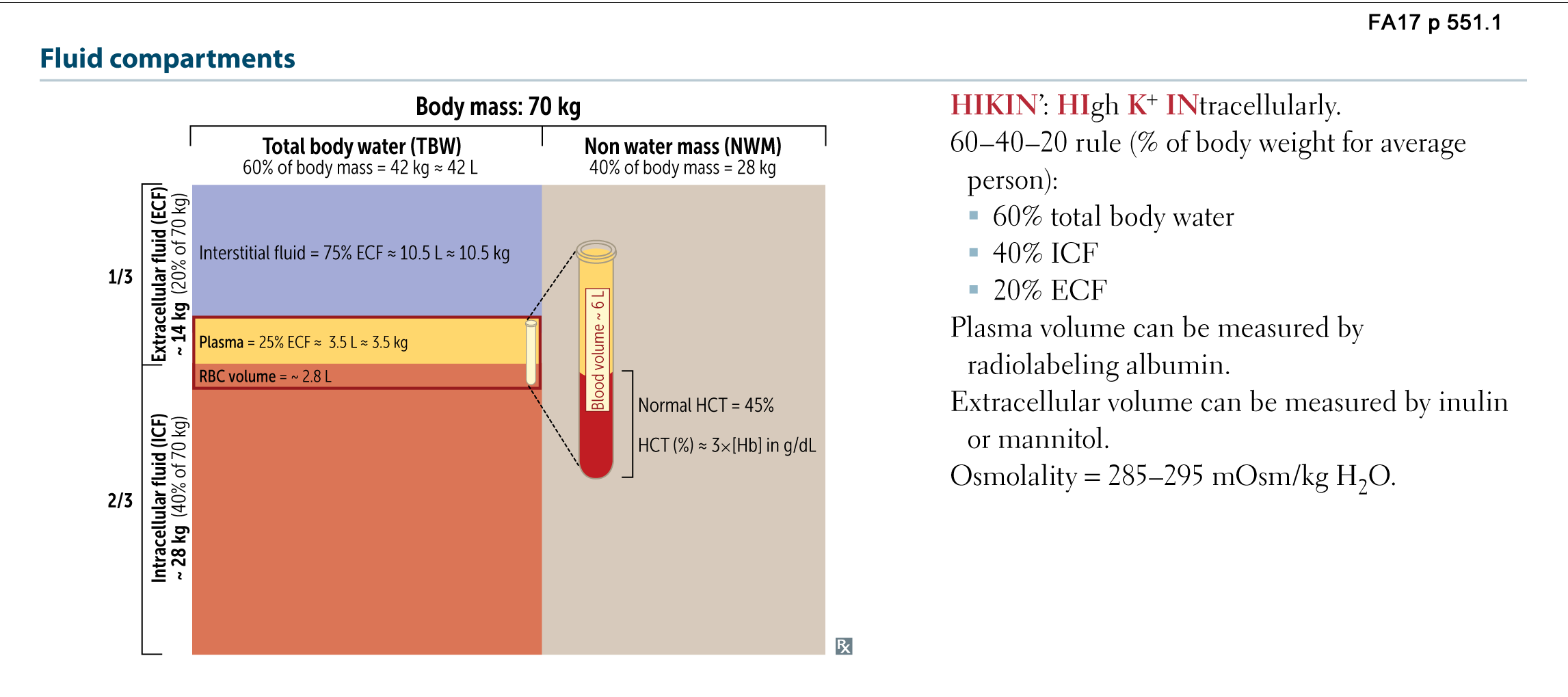
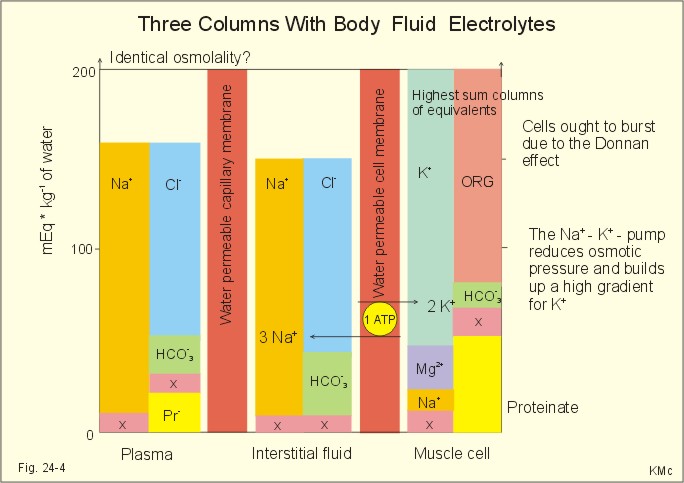
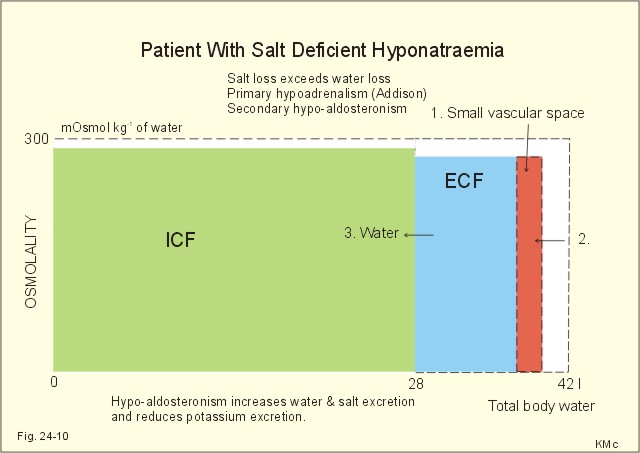
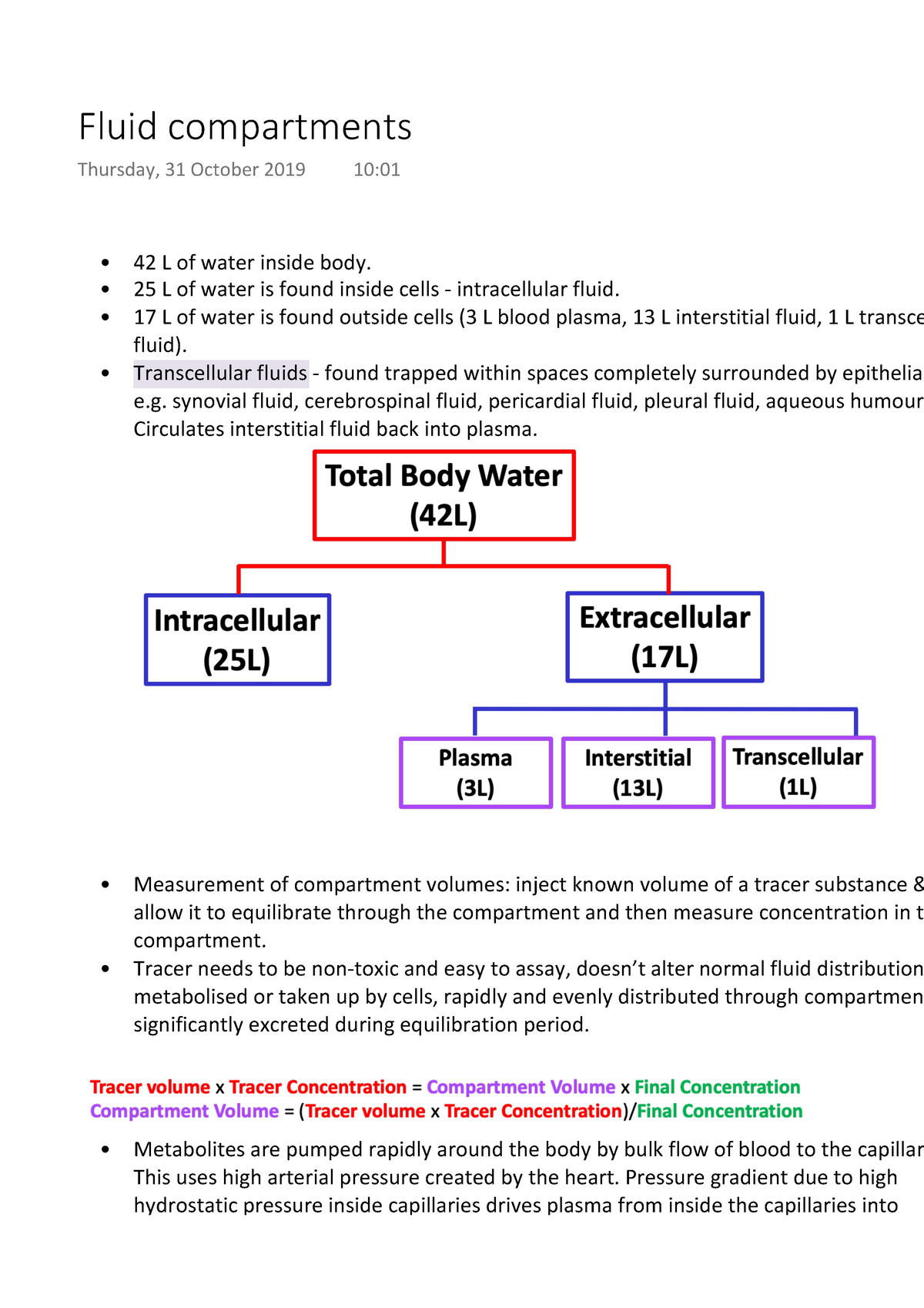
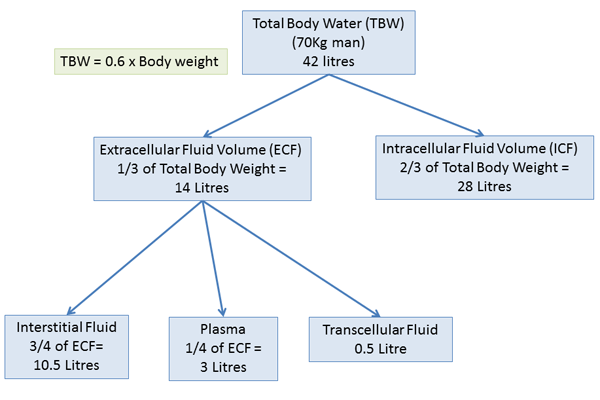
The water in the body is distributed among various fluid compartments that are interspersed in the various cavities of the body through different tissue types. Theoretically its possible to measure the size of each of the body fluid compartments by injecting substances that will stay in one compartment only the substance that attach to object.

1 Body Fluid Compartments Volume Composition Measuring
Measurement of body fluid compartments. We inject 30 ml of deuterium oxide d2o as an isotonic saline solution into an arm vein. In diseased states where body water is affected the fluid compartments that have changed can give clues to the nature of the problem. Water content regulation and measurement. For example suppose we want to measure total body water in a 60 kg woman. Compartment volumes are measured by determining the volume of distribution of a tracer substance. A known amount of a tracer is added to a compartment.
If the amount of the substance is known and the resulting concentration is measured the volume can be calculated. The tracer concentration in that compartment is measured after allowing sufficient time for uniform distribution throughout the compartment. To measure total body water heavy water deuterium oxide tritiated water hto or antipyrene a drug that distributes throughout all of the body water is used as an indicator. The volume of a fluid compartment in the body can be measured by placing an indicator substance in the compartment allowing it to disperse evenly through out the compartments fluid and then analyzing the extent to which the substance becomes diluted. The compartment volume is calculated as. The indicator dilution principle is based on the definition of a concentration.
Measurement of body fluid compartments body fluid compartments can be measured by dilution of a compound that distributes only in the space of interest.